As the world transitions to electric vehicles, the demand for batteries has skyrocketed in major automotive markets. With this increased demand, Vulcan Tool Company’s Shimmy Trim Die has provided manufacturers a way to be more efficient and reduce costs. These trimming processes have been refined over 70 years of Shimmy Die production. Vulcan Tool Company produces trimming solutions for deep drawn parts used in many industries, including aviation, medical, automobile, heavy vehicle, military, and household appliances. Decades of experience are now being used to provide trimming solutions for cutting edge battery production.
CYLINDRICAL BATTERY CELL HOUSING
Cylindrical battery cell housings have been popular for a variety of reasons. It is a simple, efficient and cost-effective design. Many applications rely on a high number of cells. The cylindrical shape of these battery cells provides strength that limits expansion that can occur as a result of extreme temperature and pressure changes. One of the first battery types to be created in large quantities, this kind is still quite popular.
There are benefits when using this type of housing for applications that require significant power. The compact design allows for many different storage configurations. Maintenance costs can also be reduced because faulty cells can be replaced individually. This proven technology has been used in some high profile electric vehicles like the Tesla Model S.
PRISMATIC BATTERY CELL HOUSING
Prismatic battery cell housings are made of carbon fiber, steel, aluminum, aluminum alloy or plastic and are designed to improve battery performance. Reliability increases because there are fewer connections in what is typically a larger housing. The housing size also helps reduce overall weight and improves battery pack efficiency.
This type of battery cell housing is becoming increasingly popular for a variety of reasons. They are strong and light, making them ideal for devices that need to be thin and where weight is an issue. They may also be modified to meet the requirements of a specific device. Producing fewer of the larger prismatic battery cells to achieve the same power output can make them more affordable.
The shape of prismatic battery cell housings allows them to be stored closely together. Power banks often use a number of prismatic cells. Some applications use cells that are interconnected by honeycomb-like channels. These channels help to protect the cells from damage caused by outside forces.
THE MAIN DIFFERENCES BETWEEN PRISMATIC AND CYLINDRICAL CELLS
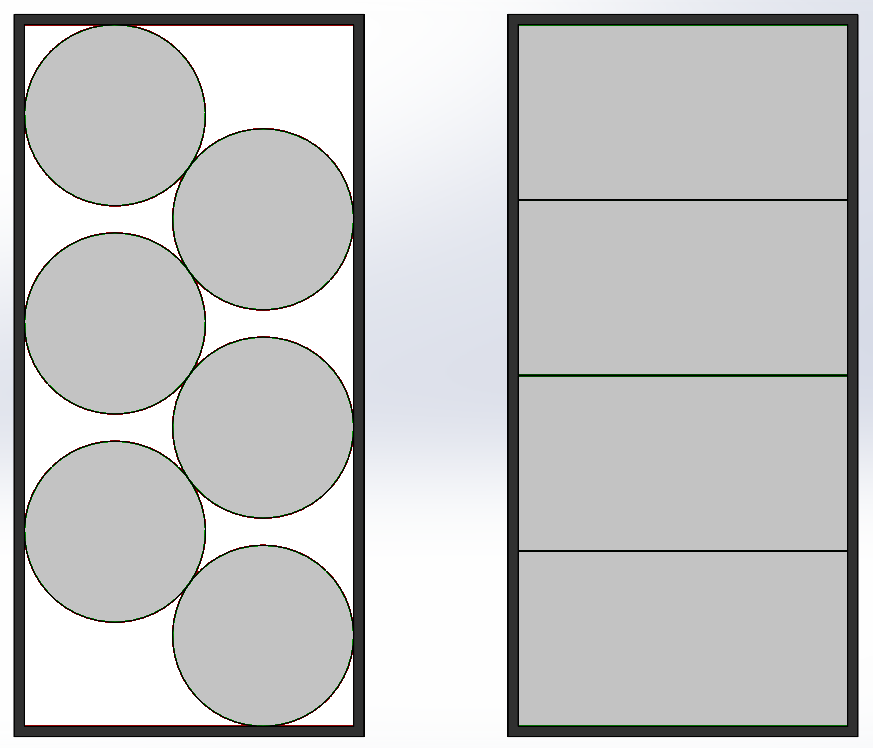
Packing principle for cylindrical cells (left) vs. the packing principle of prismatic and pouch cells (right).
Shape is not the only thing that differentiates prismatic and cylindrical cells. Other important differences include their space, power output, and cost
Space
Because of the round cross-section of the cylindrical cells, they are unable to completely utilize the space when assembled into packs and modules. The packaging density of cylindrical cells is consequently low. However, because of the space voids, coolant may more easily travel around the batteries in a pack, making thermal management of such packs simpler.
Power
Cylindrical cells may store less energy than prismatic cells, but they have more power. This means that cylindrical cells can release energy more quickly than prismatic cells. Due to this, prismatic cells are ideal to maximize energy efficiency while cylindrical cells are ideal for high-performance applications. Cylindrical cell applications are more reliable because when one cell goes bad in a battery built with Cylindrical Cells the effect is small whereas a Prismatic Battery would be left unusable in most cases.
Cost
Prismatic and Cylindrical battery cells are more suited for different chemical applications. Those most suited for Prismatic cells are less expensive initially, but have higher lifetime costs currently. With advancements in battery composition, this difference may change. At the moment, Cylindrical battery cell applications are typically less expensive over the life of the product.
MANUFACTURING AND TRIMMING OF THE PRISMATIC AND CYLINDRICAL BATTERY CELL HOUSINGS
The manufacturing of Prismatic and Cylindrical battery cell housings is intended to make the housing strong enough to protect the cells from physical damage and from the corrosive environment that the battery will be subjected to. It must also be able to withstand the high temperatures that the battery will experience.

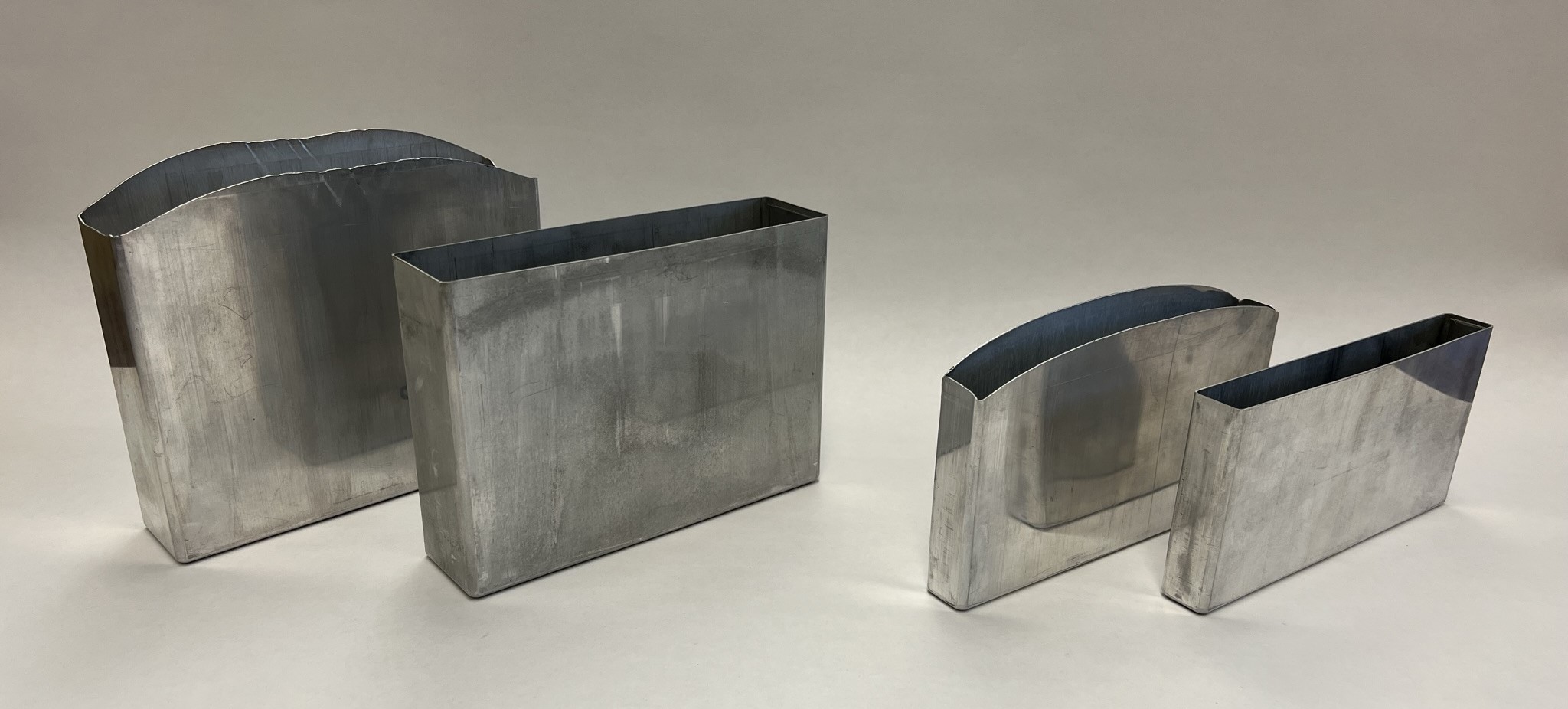
A 3″ Shimmy Trim Die
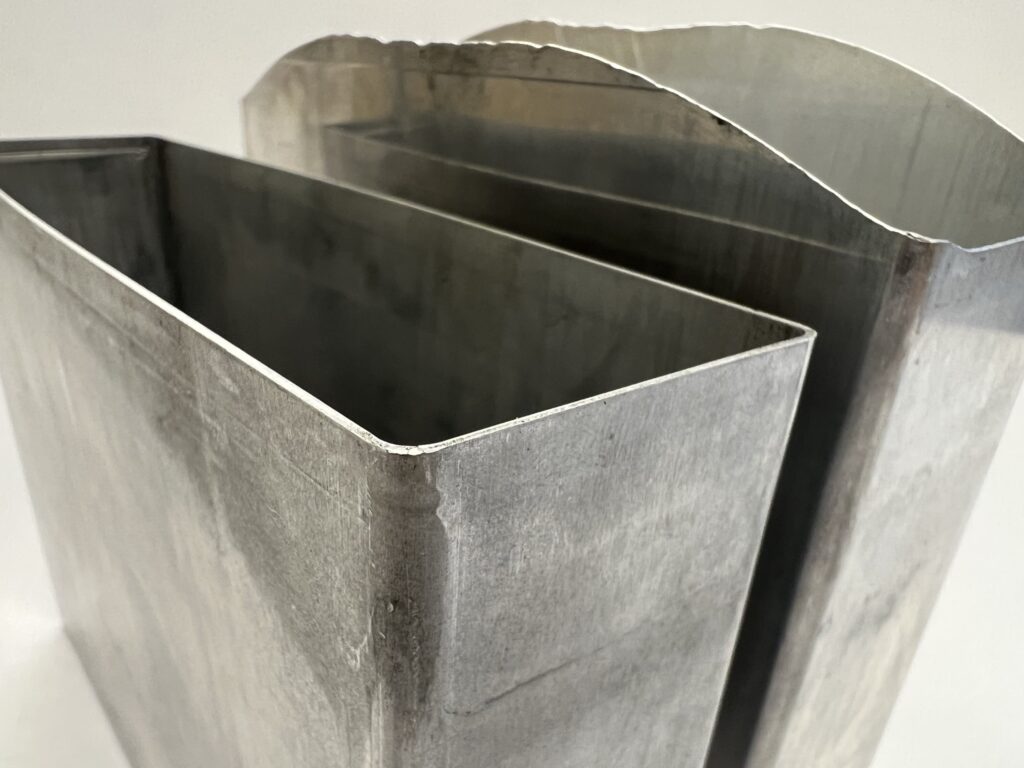
Once the cell housing is drawn a transfer process is typically used to place the housing in a Shimmy Trim Die so it can be trimmed.
The Shimmy Die can trim an entire drawn part in one press stroke while controlling flatness and height. It can also trim with notches or irregular heights as needed. The master die can also be used with new tooling to trim other parts that are similar in size.
Brehm Shimmy Dies can be custom built to fit almost any application and to trim or profile any drawn shell to precision tolerances. Horizontal type dies can also be punch press driven which may become more economical for longer parts not suitable for vertical press orientation. Vertical dies can also be used with existing hydraulic or mechanical press for shorter tubular components or drawn stampings.



